Understanding Keratoconus: Causes, Symptoms, and Risk Factors
Introduction
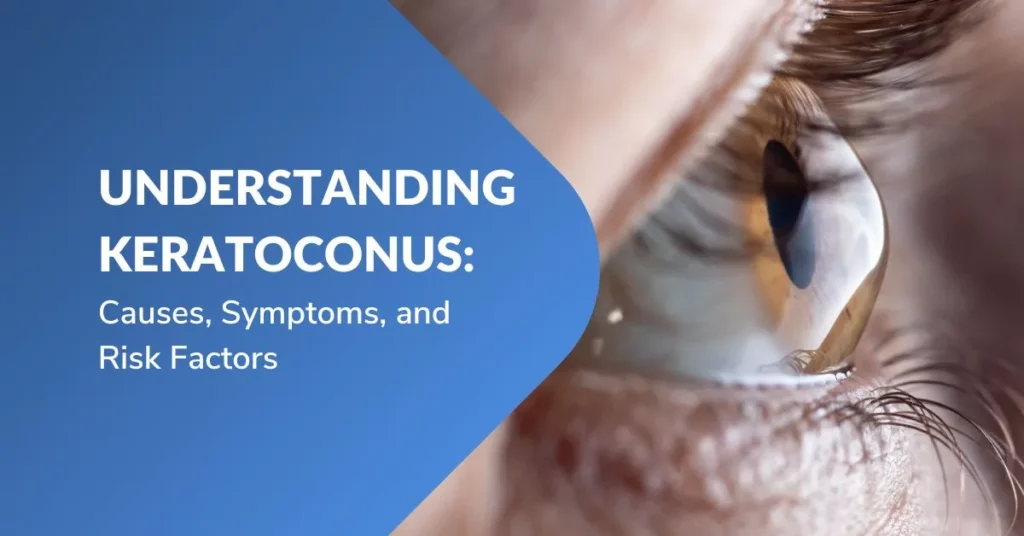
Keratoconus is a condition that affects the cornea, the transparent outer layer of the eye. It causes the cornea to gradually thin and bulge into a cone-like shape, distorting vision and making it difficult to see clearly. The condition typically develops during adolescence or early adulthood and affects around 1 in 2,000 people.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and risk factors associated with keratoconus can help individuals recognize the signs of the condition and seek appropriate treatment at Global Eye Hospital Kukatpally, Global Eye Hospital Narsingi.

Causes:
The precise cause of keratoconus is unknown, but it is credited to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some studies have shown that certain genes may make individuals more susceptible to developing the condition. Other factors that may contribute to the development of keratoconus include chronic eye rubbing, allergies, and poorly fitting contact lenses.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of keratoconus can vary depending on the severity of the condition. In the early stages, individuals may experience blurry or distorted vision, sensitivity to light, and increased difficulty driving at night. As the condition progresses, vision may become even more distorted, making it difficult to read or recognize faces. Some individuals may also experience eye strain or headaches.
Risk Factors:
While the exact cause of keratoconus is unknown, there are several risk factors that may increase an individual’s likelihood of developing the condition. These include:
- Genetics: Keratoconus tends to run in families, and individuals with a family history of the condition are at an elevated risk of developing it themselves

- Age: Keratoconus typically develops during adolescence or early adulthood, although it can occur at any age.
- Gender: Men are marginally more likely than women to suffer from keratoconus.
- Eye rubbing: Chronic eye rubbing, such as that associated with allergies, can contribute to the development of keratoconus.

- Other medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as connective tissue disorders, Down syndrome, and sleep apnea, may increase an individual’s risk of developing keratoconus.
Treatment:
The treatment options for keratoconus depend on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, glasses or contact lenses may be sufficient to correct vision. In more severe cases, however, other treatment options may be necessary.
One common treatment for keratoconus is the use of special contact lenses called scleral lenses. These lenses are larger than traditional contact lenses and sit on the sclera, the white part of the eye, rather than the cornea. This can help to reduce the distortion of the cornea and improve vision.
In some cases, an operation may be quintessential to treat keratoconus. One surgical option is corneal cross-linking, which involves the use of ultraviolet light and a special solution to strengthen the cornea and prevent further thinning.
Conclusion
In conclusion, keratoconus is a condition that affects the cornea and can lead to distorted vision. While the exact cause of the condition is unknown, there are several risk factors that may increase an individual’s likelihood of developing it. Understanding the symptoms of keratoconus and seeking appropriate treatment can help minimize the impact of the condition on an individual’s vision and quality of life. For keratoconus treatment in Hyderabad, best ophthalmologist in Hyderabad can be found at Global Eye Hospital Kukatpally.
Book your appointment now for all eye-related services.
Your Vision Our Focus


